CREATURE
- HOME
- CREATURE
Examples of analysis
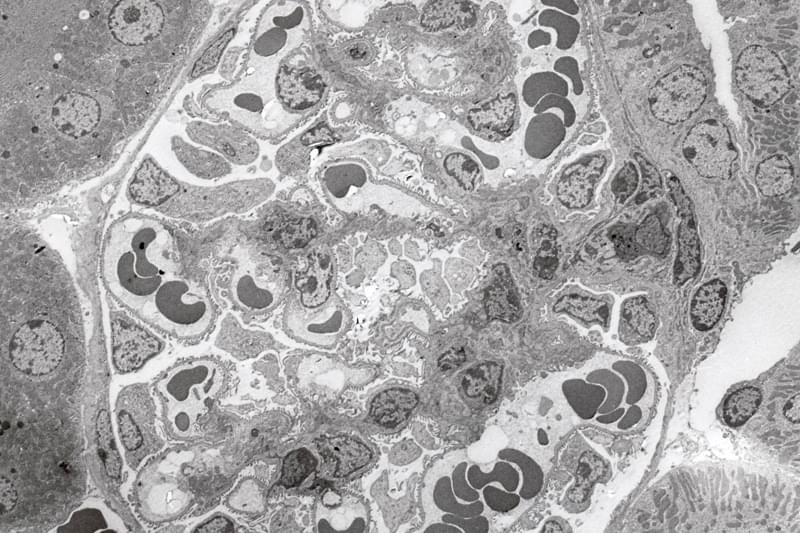
Hepatocytes (pig liver)
x7.000 Inserted images of cell membranes (x100,000)
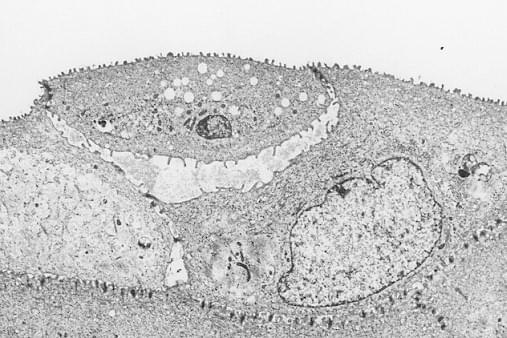
- The liver’s many functions include lipogenesis, protein synthesis, drug metabolism and removal, energy storage, etc. Hepatocytes constitute the bulk of the liver, but bile capillaries (BC) and blood vessels (HS) are also present, and blood cells (EC, Kf) are seen inside blood vessels.
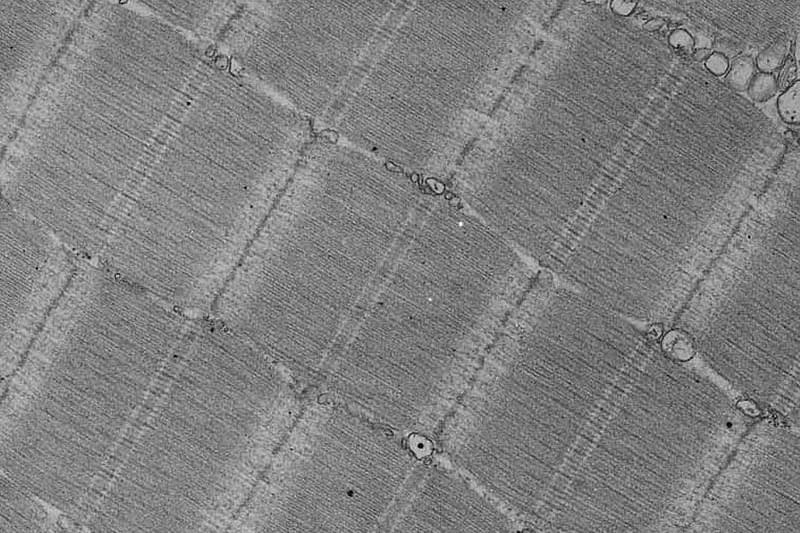
- Each hepatocyte is surrounded by a cell membrane (CM) and has one cell nucleus (N). Cytoplasm is made up of endoplasmic reticulum (rER), which is responsible for protein synthesis, mitochondria (M) for producing cellular energy, and glycogen (Gl) for storing glucose. The inserted image shows the expanded view of cell membranes of adjoining cells, and it shows that each membrane is 7 nm wide and has a double-layer structure.
- The hepatocyte is often used as an example when explaining the structure and functions of a common cell because it contains typical cell organelles.
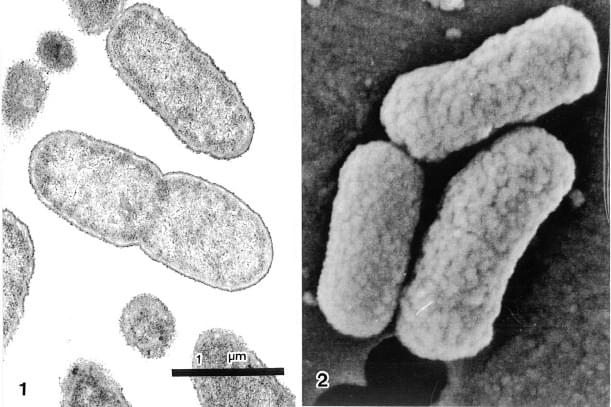
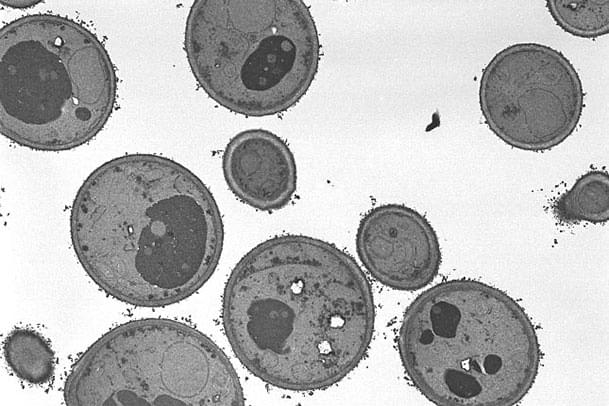
Pathogenic Escherichia coli O157 x30,000 1:TEM 2:SEM
O157 is a bacterium that became known as one of causative bacteria of mass food poisoning in recent years. It is urgently needed to understand its production mechanism of the Vero toxin. Bacteria have cell walls around them, making it difficult for chemicals such as the fixative to penetrate. Although the sample preparation method is basically identical to that for animal tissues, image quality can be enhanced by adding extra process time to steps and performing fixation at room temperature.